综述
Personal LLM Agents: Insights and Survey about the Capability, Efficiency and Security
数据集
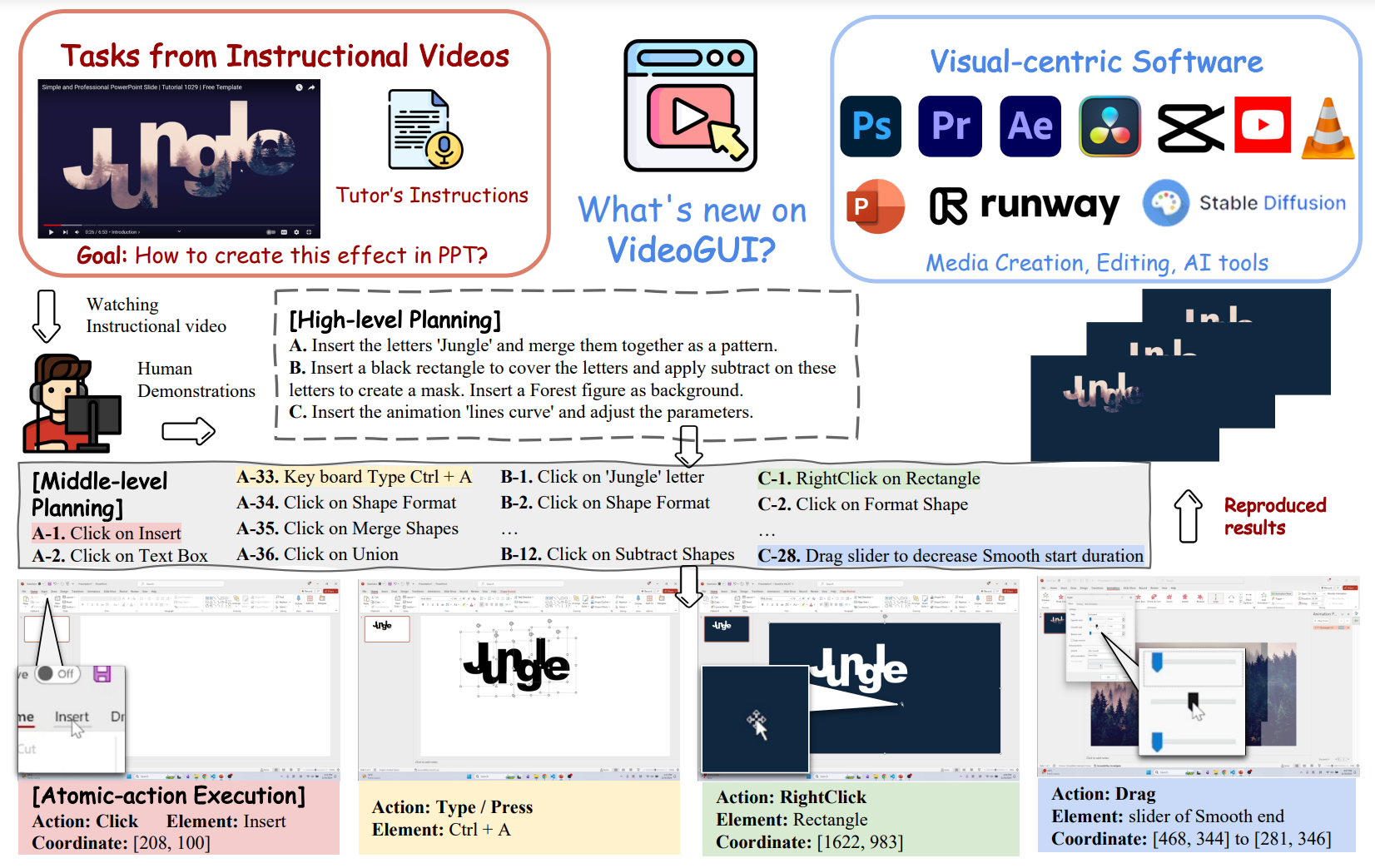
VideoGUI: A Benchmark for GUI Automation from Instructional Videos,把 GUI 能力划分为三层:High Level 表示高层次的操作意图。Middle Level 为用自然语言描述的单步操作,Atomic-action 为使用固定格式描述的准确操作。整个 pipeline 都是人标的,包括视频挑选,标注,验证,task 数量较少,86 个 full task,463 个 subtask。
GUI-WORLD: A Dataset for GUI-oriented Multimodal LLM-based Agents,从 Youtube 上爬取视频数据+人类录频操作数据,提取关键帧,以及 QA 文本。关键帧的标注由人类完成,包括:执行的操作, 关键帧转移的目标,使用的软件或者网站,鼠标操作,键盘输入等。迷惑的是为什么人类操作还要录屏,既然最后是提取关键帧,那可以直接在人操作的时候提取关键帧?
谷歌: Onthe Effects of Data Scale on Computer Control Agents,在安卓场景下人标gui sft数据,有测试集
谷歌:Android in the Wild: A Large-Scale Dataset for Android Device Control
输入为 image 和 text instruction。包含 30 K 的数据,Google Apps 的占比最大。

World of Bits (WoB): Use only keyboard & mouse,输入为彩色图像,DOM 文档,请求。支持通过众包构造新的数据。
OpenAI Universe: Game, Web tasks,输入数据只有图像,操作键盘和鼠标。
AndroidEnv: A Reinforcement Learning Platform for Android: 在 android emulator 上运行的虚拟环境。
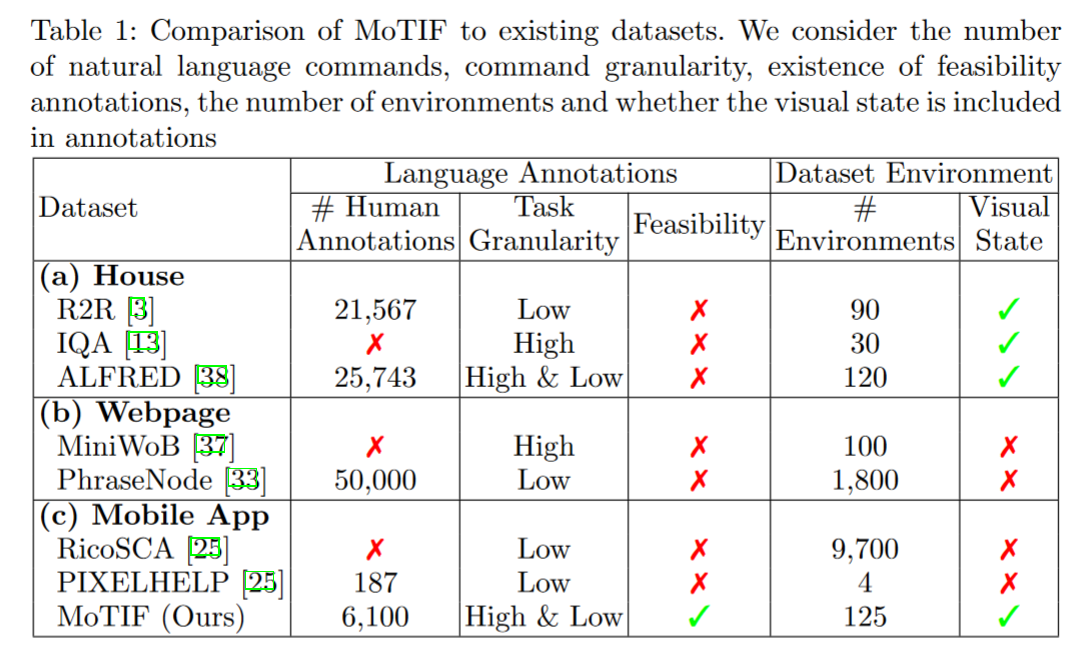
(MoTIF)A Dataset for Interactive Vision-Language Navigation with Unknown Command Feasibility:人类标注,有 feasible 字段。
PIXELHELP: Mapping Natural Language Instructions to Mobile UI Action Sequences
模型
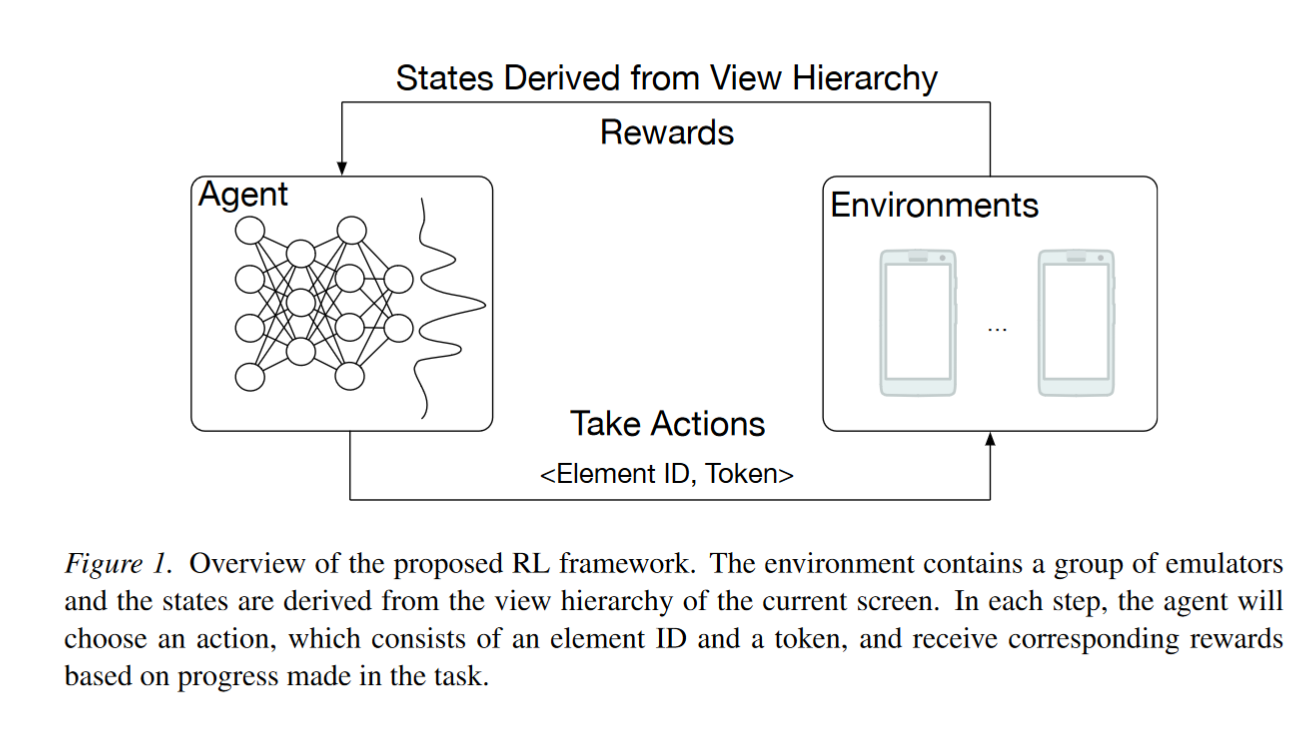
RL-based method
中间步骤奖励非常重要。稀疏奖励下从0训练容易停滞不前,需要先行为克隆提升一定的性能,再执行 RL 算法。
泛化性差,不像 LLM 具有大量先验知识。
App-Buddy: PPO based method, Interact with DOM.
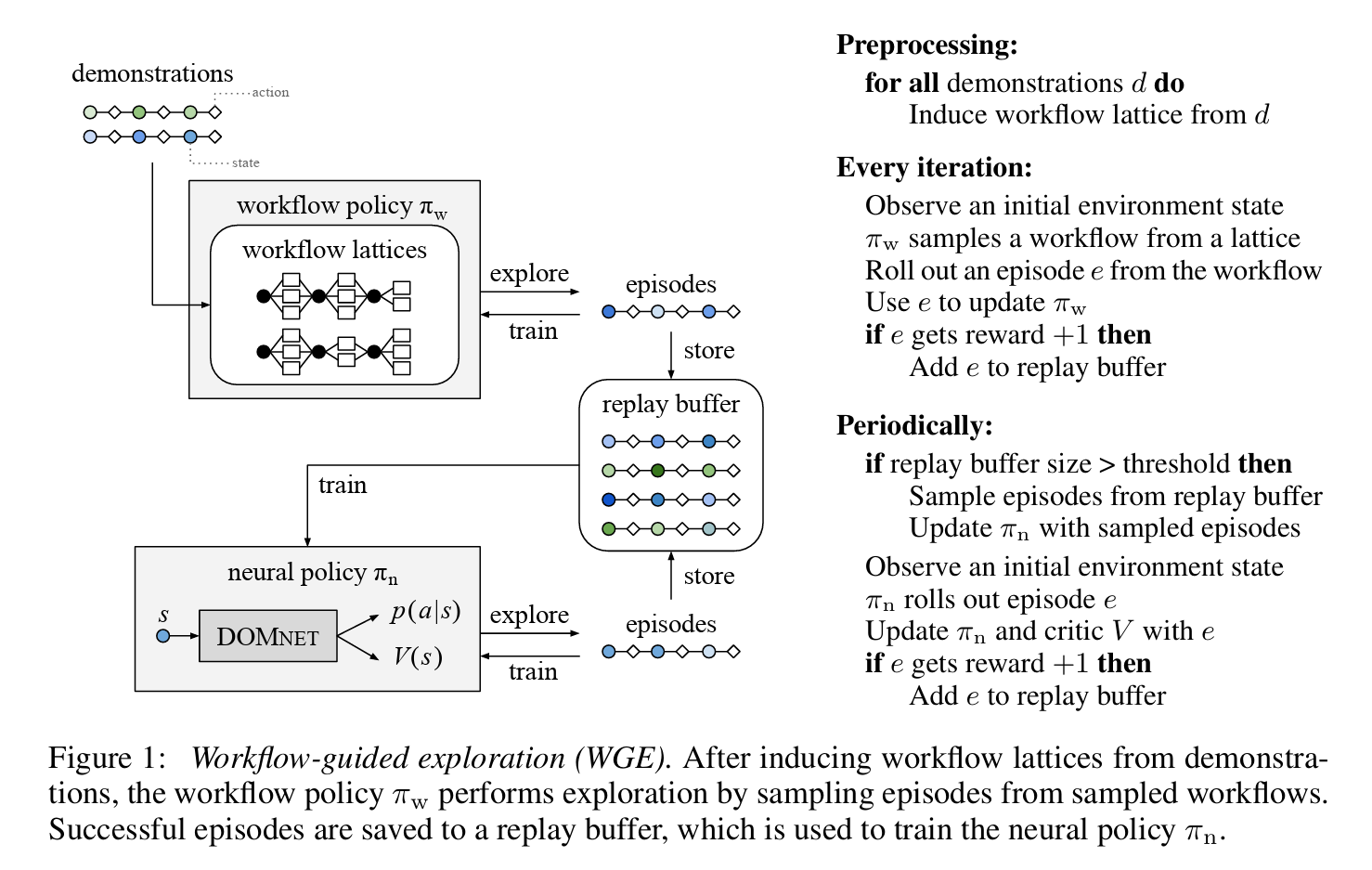
REINFORCEMENT LEARNING ON WEB INTERFACES USING WORKFLOW-GUIDED EXPLORATION: 稀疏奖励下从0训练容易停滞不前,需要先行为克隆提升一定的性能,再执行 RL 算法。但是 BC 方法容易过拟合,因此通过从示例中导出 workflow policy,再从 workflow policy 中采样新的 policy 的方法来获取新的 trace。
LLM Agents
Prompt Engineering
Explore, Select, Derive, and Recall: Augmenting LLM with Human-like Memory for Mobile Task Automation,从 trace 中学习 subtasks,然后封装成 api,在后续执行任务时可以直接调用。也是纯文本推理。
M3A,SeeAct 都是采用截图标注,然后推理,速度会慢很多。
AutoDroid: LLM-powered Task Automation in Android (MobiCom 24)
Exploration + Execution 范式,基于 VH/DOM 的 UI 表示。
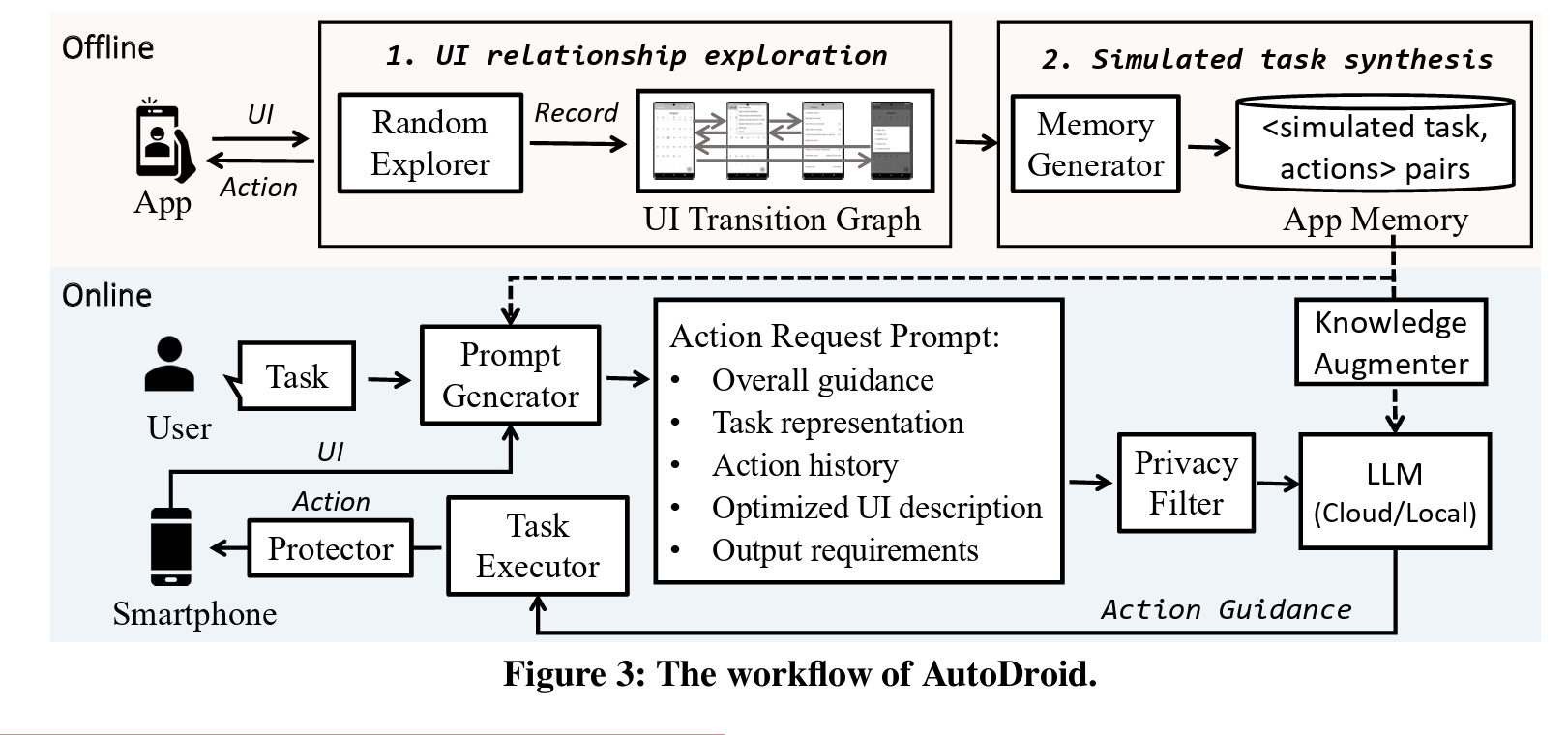
GPT4 成功率相当可观,finetune小模型的效果接近 GPT 3.5:
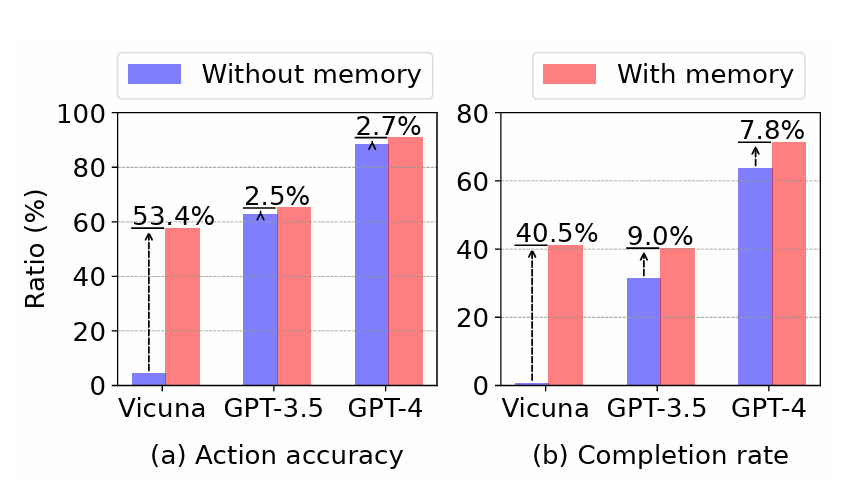
离线部分:随机探索 + 生成 App Memory,对 UTG(UI Transition Graph) 进行分析,LLM 生成每个页面和每个 UI 元素的描述,并构建 embedding vector base。
在线部分:根据 embedding vector base 筛选 UI 元素,只留下那些重要的 UI 元素,并且利用 APP Memory 中的元素生成 Guide 辅助模型进行决策。
Responsible Task Automation: Empowering Large Language Models as Responsible Task Automators
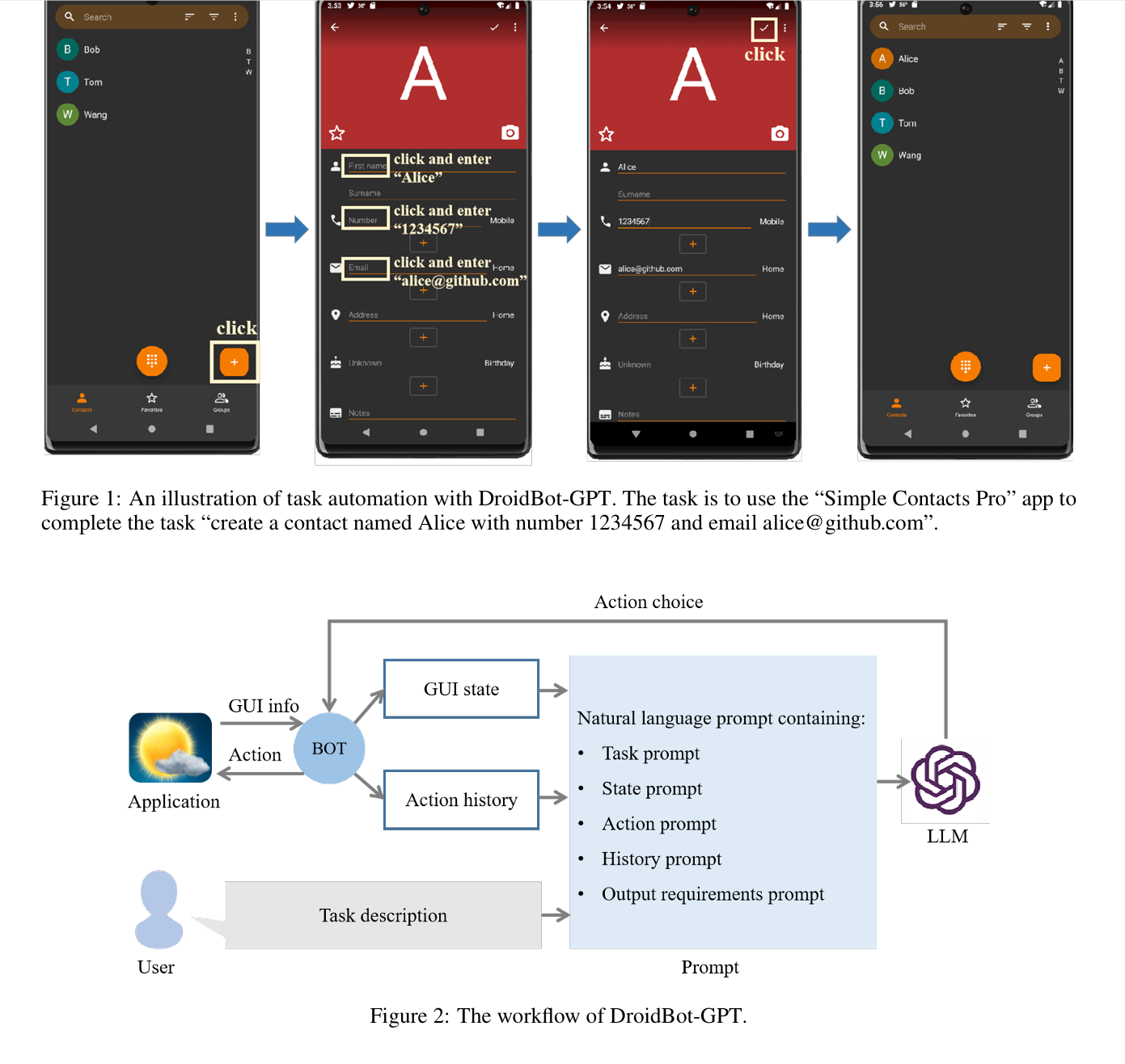
DroidBot-GPT: GPT-powered UI Automation for Android
AppAgent: Multimodal Agents as Smartphone Users:利用 GPT4-V 进行探索+部署,支持 learn from demonstration。
Multimodal
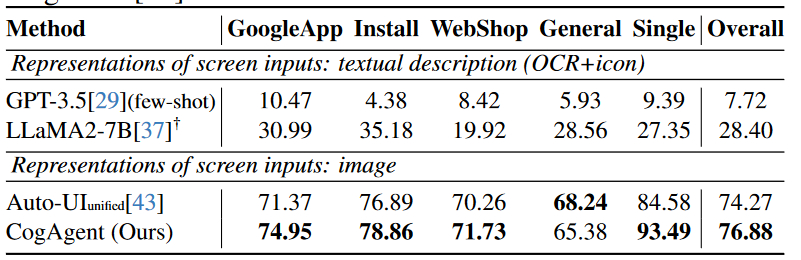
CogAgent: A Visual Language Model for GUI Agents,从结果来看 Auto GUI 还是挺能打的,700M 的 encoder-decoder 和 18B 的 CogAgent (CogVLM-17B 改造而来)不相上下。
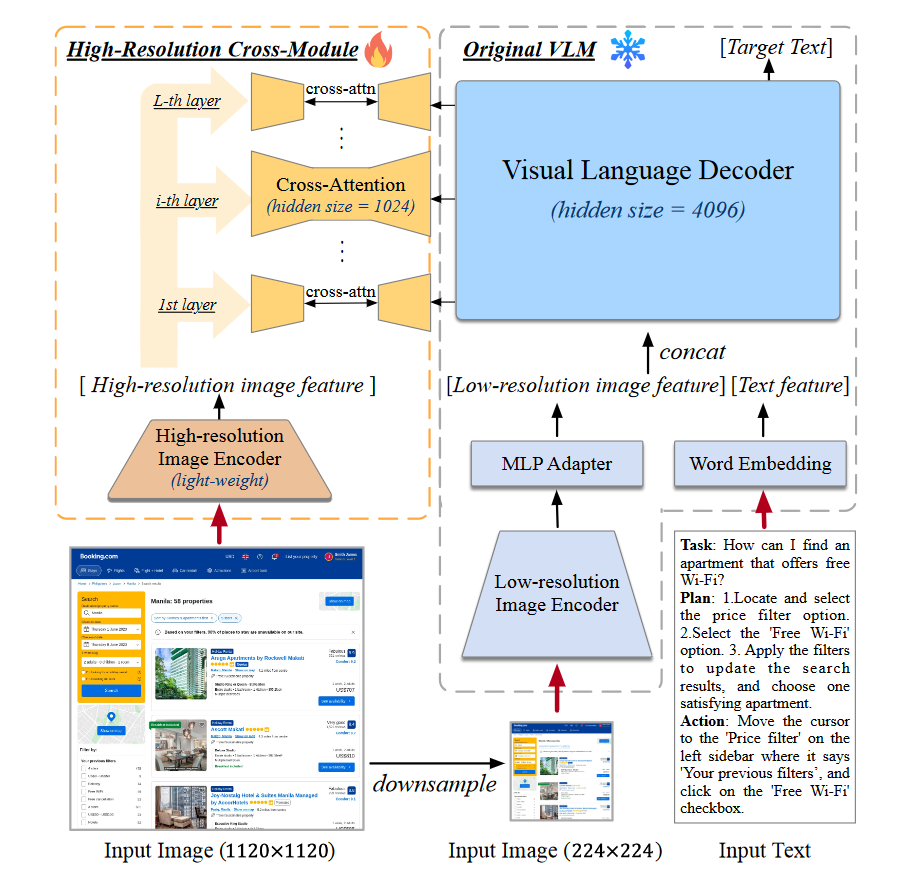
模型架构如下。设计上采用一个低分辨率的图像编码器来识别大部分 UI 元素和布局,高分辨率的编码器用来识别文字(这个有证据吗?仅仅有一个简单的消融实验)。比较反直觉的是,在 OCR 领域模型应该采用更小的隐藏层,而不像通用领域那样需要很大的隐藏层,所以高分辨率编码器反而参数更少,只有 0.30 B。而且,这东西每层都跟 Decoder 做特征融合,不直接使用高分辨率是因为 CogVLM 原来的架构就支持 224*224(经典数字),太大了在 Self Attention 阶段计算量会爆炸,所以这里通过压缩隐藏层大小 + Cross Attention 来降低计算量。
对齐方面,人标了2k条,然后把 Mind2Web 和 AITW 的数据拿过来用 GPT-4 标了 VQA 的数据集。
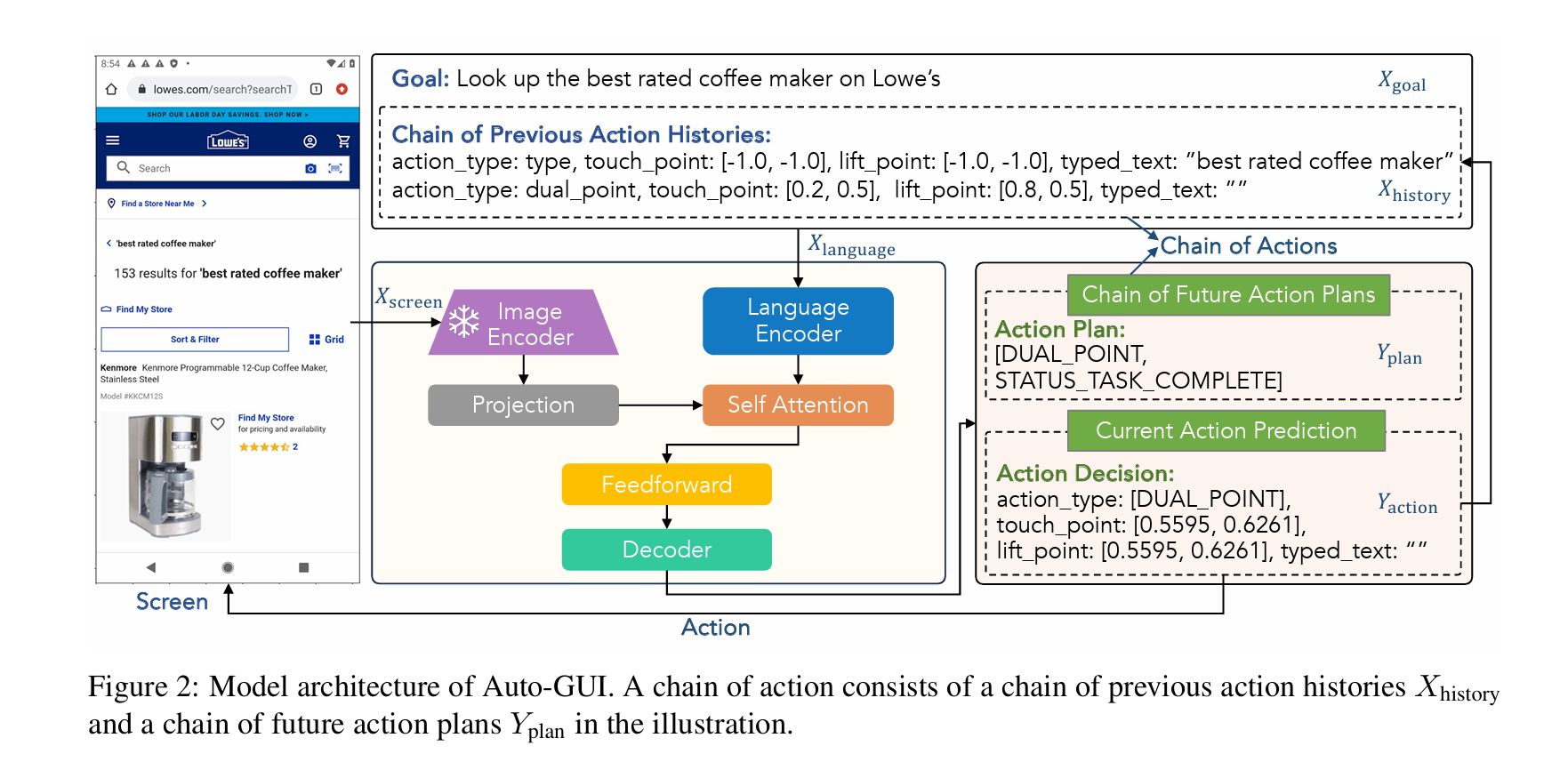
输出格式包括 Plan,Action,Operation,Operation 部分同样是让大模型生成操作和坐标数据,我依然很好奇到底 VLM 能不能理解坐标信息。
Auto GUI: You Only Look at Screens: Multimodal Chain-of-Action Agents
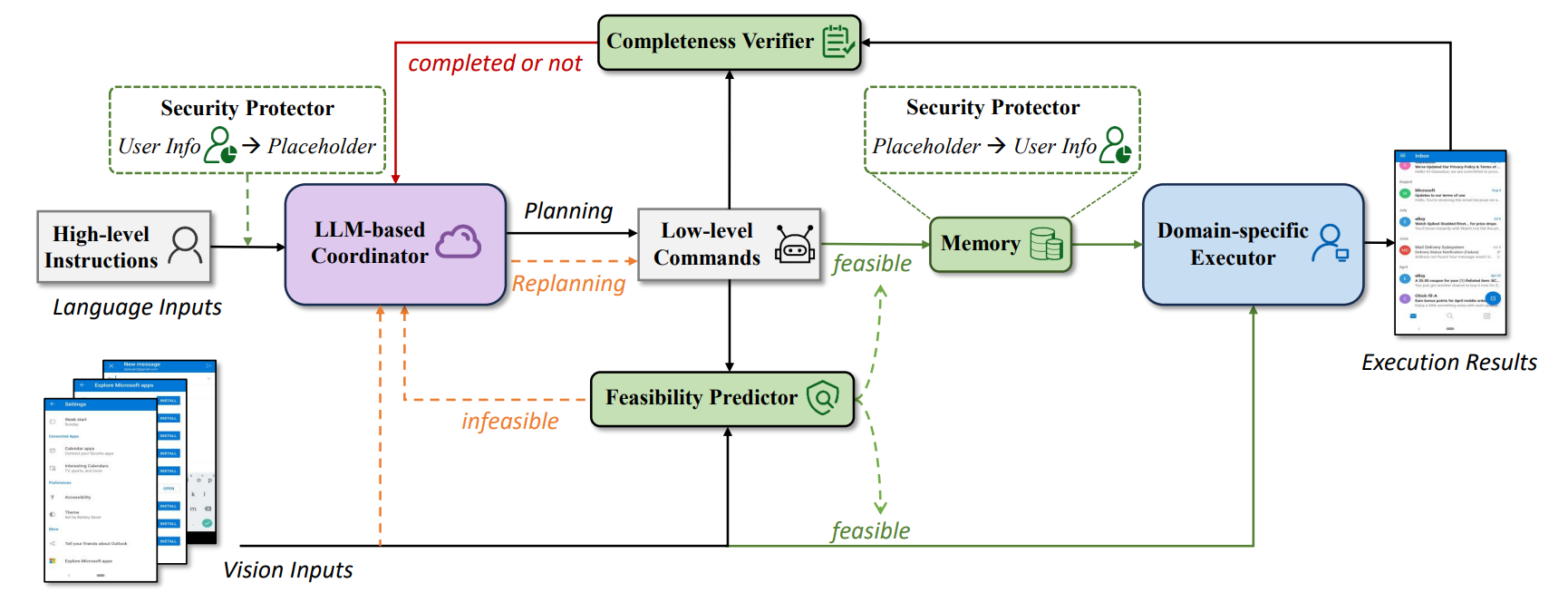
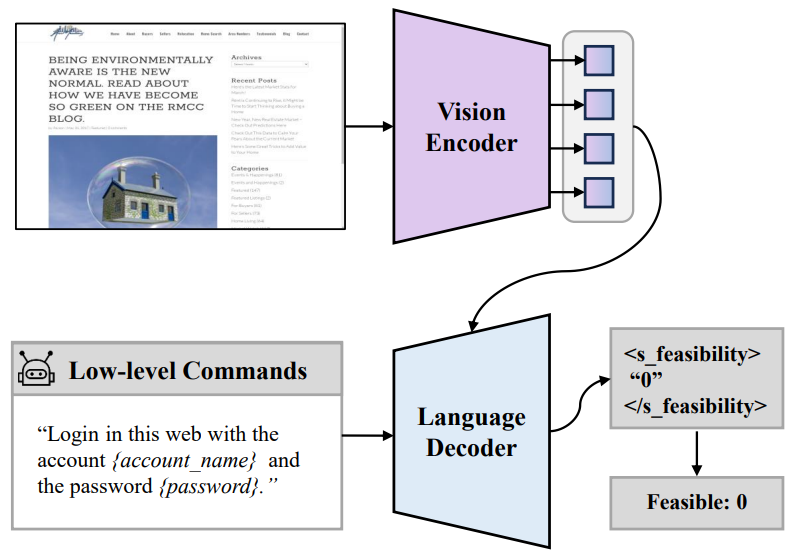
微软 Responsible Task Automation: Empowering Large Language Models as Responsible Task Automators,大小模型协同,一个模型负责 planning,一个模型负责 executing,同时,在这个过程中实现隐私保护。这个过程会通过一个语言模型根据屏幕截图 + low level commands 来判断命令是否可执行、是否执行成功。当然,仅仅用 Decoder 做二元判断似乎有点浪费,感觉是个分类器就能做,用 bert 说不定更好。另外,Vision Encoder 在识别图片中文字这一块擅长吗?模型架构来自于 pix2seq,它原本是做目标检测的。
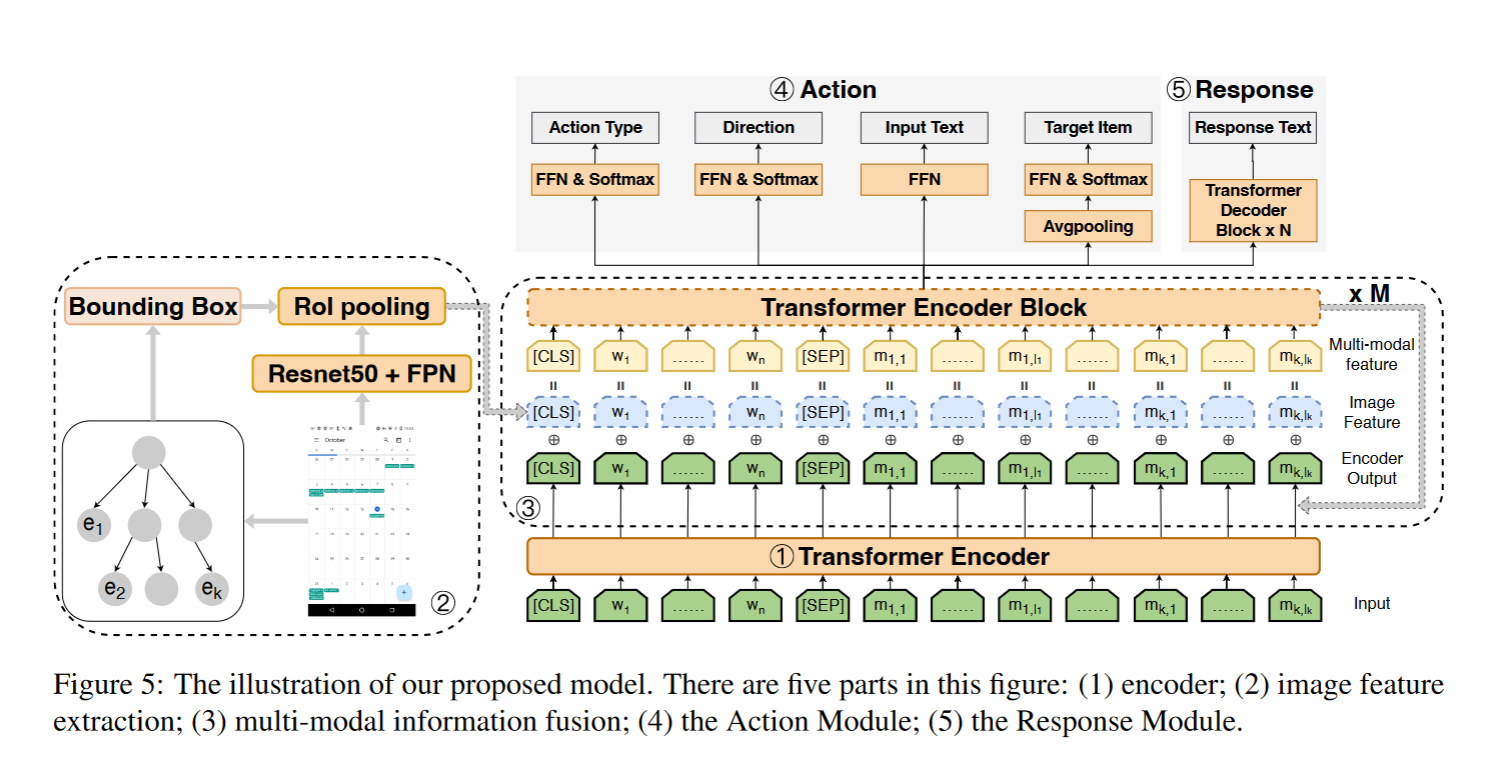
META-GUI: Towards Multi-modal Conversational Agents on Mobile GUI
UI Understanding and Representation
ActionBert: Leveraging User Actions for Semantic Understanding of User Interfaces:UI 理解,leveraged the temporal con
nections between UIs in a UI sequence to design their pretraining tasks
UIBert: Learning Generic Multimodal Representations for UI Understanding:self-alignment among different multimodal features in a single UI, use trainable lightweight encoders
LLM + RL
Enabling Intelligent Interactions between an Agent and an LLM: A Reinforcement Learning Approach
Code-based Methods
Topics
长序列的任务执行
多模态 GUI Agent
隐私保护
用户偏好/个性化的 Agent
Proactive Agent
Show me how to do/高效的策略更新方法
RL training in sparse reward
LLM as Reward Model
Action & Workflow embedding
寻找 UI 的表征/ UI Understanding
Paper Reading
20240725
ShareGPT4Video: Improving Video Understanding and Generation with Better Captions:视频数据理解,或许有助于 GUI Agent 的训练。提出了一个 Differential Sliding-window Captioning 的方案,让 GPT4o 根据上一帧和当前帧之间的差别来输出 Caption,最后加上一个 Summary 来描述整个视频的 pipeline。这里的关键是如何选关键帧,原文采用一个 CLIP Model,通过比较最后一帧和这一帧的相似性,选出差别较大的帧。
Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision
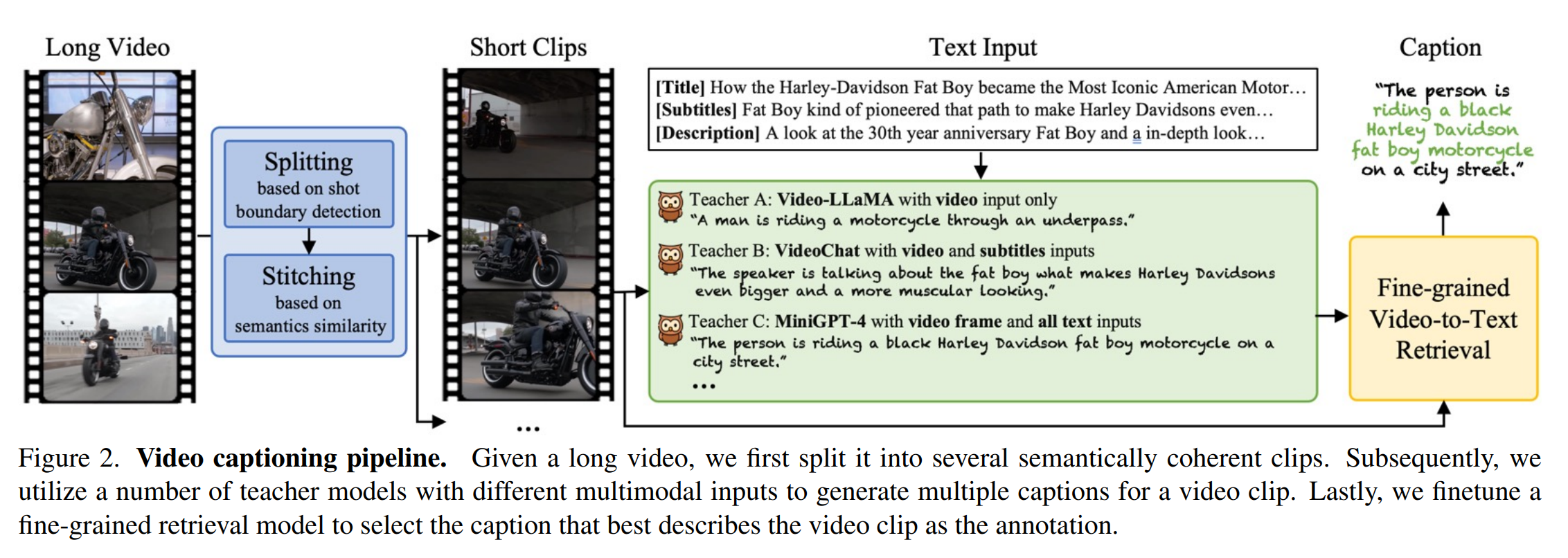
Panda-70M: Captioning 70M Videos with Multiple Cross-Modality Teachers
20240629
Read Agent:利用分页解决大模型长文本表现差的问题(Lost in middle)。
大小模型协同
SwiftSage: A Generative Agent with Fast and Slow Thinking for Complex Interactive Tasks。用 BC 的小模型进行 fast thinking, 然后让大模型进行 slow thinking / grounding.
Code Policy
AdaPlanner: Adaptive Planning from Feedback with Language Models
Code as Policies: Language Model Programs for Embodied Control: 2209.07753, Use Code (Formal Language) in Embodied Agent.
FFN 的作用
Transformer Feed-Forward Layers Build Predictions by Promoting Concepts in the Vocabulary Space
Dissecting Recall of Factual Associations in Auto-Regressive Language Models
杂项
MatFormer:嵌套训练 FFN 参数,适配不同的设备。
SADMoE:对 weight 聚类,将双层 MLP 转为 MoE
Deja Vu:预测 attention 的激活值,动态分配空间